Startups need to build a solid business plan to succeed in entering a new market. Using the right business helps startups become sustainable and overcome market obstacles. Entrepreneurs often need help to choose a suitable startup business model because there are too many options.
Despite so many options, the skepticism of whether a startup business model will work makes the decision complex. Plus, if you don’t choose a suitable business model, it can be economically and operationally disastrous.
The right choice of startup model can take your business to a unicorn level. According to a report, the total number of unicorns in 2023 was 1,361, 29% higher than in 2022.

Getting your startup business model right is crucial to creating the next giant unicorn. This blog post will help you choose the most appropriate business model, its significance, and examples of successful startups.
What Is the Significance of a Startup Business Model?
A business’s business model outlines how it generates and extracts value. Ensuring income and operational sustainability is crucial for startups.
Here are the critical aspects of a business model:
- Identifies target customers and their needs
- Outlines value propositions and unique selling points
- Defines revenue streams and cost structures
A robust startup business model adapts to market changes, providing resilience. This adaptability helps attract investors and stakeholders. It ensures the efficient allocation of resources and efforts.
For example, consider a SaaS startup offering a project management tool for industrial manufacturers. The startup business model would identify key customers like mechanical engineers and operations managers.
It would outline unique features such as real-time collaboration and industry-specific templates. Revenue would come from subscription fees, and the cost structure would be scalable based on user numbers.
For digital marketers, a solid business model enhances marketing strategies. It aligns marketing efforts with overall business objectives. This alignment maximizes the impact of marketing campaigns.
What Are the Different Types of Business Models for Startup?
Business models are the backbone of any successful startup. Understanding various models can help entrepreneurs make informed decisions. Here are the different business models for startups that can guide your business strategy.
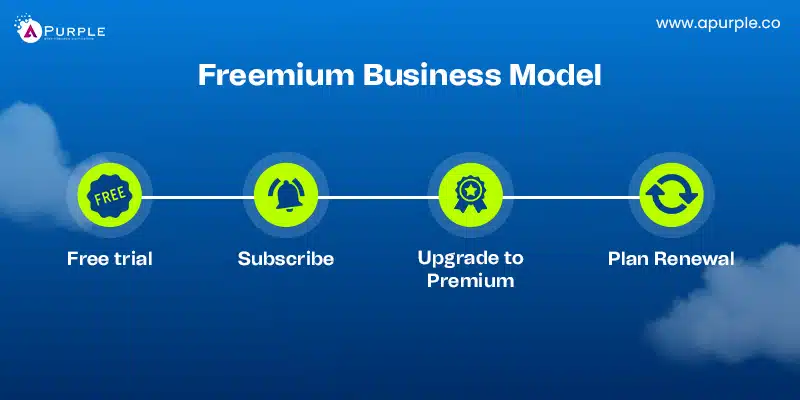
1. Freemium Business Model
The freemium business model charges for advanced features but provides essential capabilities for free. Users can experience the product before deciding to upgrade. Many Lean Startup Methodology approaches include freemium as a popular choice to validate ideas with minimal investment and gather real user feedback early on.
Companies using this model carefully balance free and paid features. They aim to provide value in the free version while incentivizing upgrades.
Companies using the freemium model:
- Dropbox
- Hulu
- Zoom
- Canva
Hulu is a streaming service company that also uses a slightly different version of the freemium model. It offers a free service with ads and a paid service without ads. Some of Hulu’s strategies include exclusive content and live TV in the higher tiers of the plans.
It is a practical business model for SaaS firms, streaming services, and apps because it enables users to feel the product’s value before they upgrade.
The freemium model is only viable for businesses that have high production costs, tangible products, or services that require capital intensiveness.
Businesses in manufacturing, traditional retail, and bespoke services may find it difficult, as providing free tiers may not be financially feasible.
2. Subscription Business Model
Subscription models provide ongoing access to products or services for recurring payments. Customers benefit from regular updates and uninterrupted service. This approach ensures companies’ predictable revenue streams.
Companies using the subscription model:
- Teladoc
- Adobe Creative Cloud
- The New York Times
- Microsoft Office 365
Teladoc offers virtual medical consultations and health management services. Teladoc’s subscription model provides subscribers with convenient access to healthcare professionals. The company continually expands its services to address various health needs. Teladoc’s subscription approach has helped it grow in the digital health market.
The model works well for content creators and e-learning platforms. It is also a good business model for a startup company aiming for steady cash flow and growth.
This model is less suitable for businesses selling one-time purchase products or high-cost items. It fits poorly with companies requiring substantial initial investment per customer.
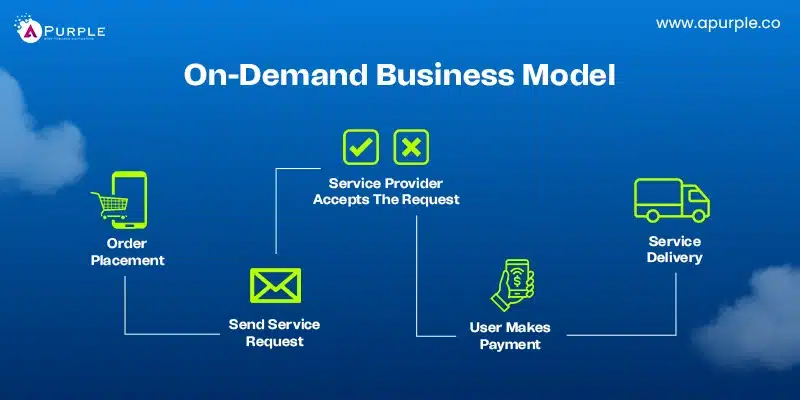
3. On-Demand Business Model
On-demand business models involve meeting the customer’s needs for services or products with an immediate solution. This strategy uses advanced technology to meet the customer’s needs within the shortest time possible.
These businesses mainly function through applications available on mobile devices or through the website. They depend on a chain of agents, dealers, or sub-agents. Sometimes, the prices in such a business model may vary depending on the service demand, time frame, and availability of tools and equipment.
Companies using the on-demand model:
- Doordash
- Airbnb
- TaskRabbit
- Bolt
- Uber
DoorDash, Bolt, and Uber are instances of incredibly prosperous on-demand companies built on a scalable on demand app solution. One of the services that primarily links customers and restaurants in the food delivery sector is DoorDash. Bolt provides ride-hailing and micro-mobility services in multiple countries.
Uber offers ride-hailing, Food delivery, and freight services worldwide. These companies integrate technology to improve their operations and users’ experiences.
This model suits organizations with easily scaled-up technology platforms and service providers that can be adjusted quickly. It is inappropriate for companies that initially need to raise significant capital or sell goods that generate low-profit margins.
High operational costs and other problems, such as logistical issues, can also make it unfit for specific industries.
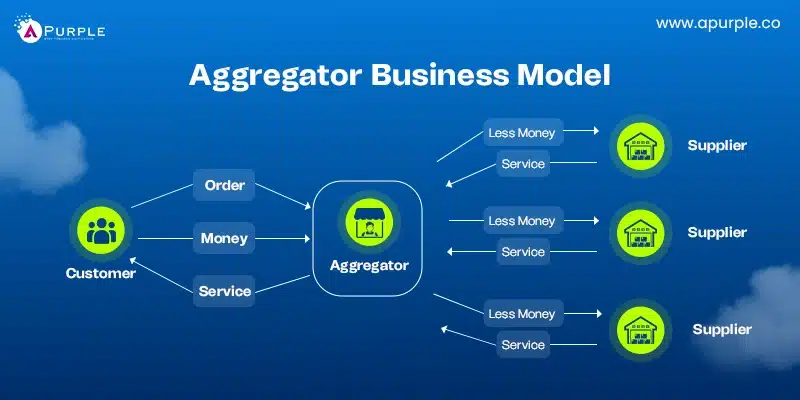
4. Aggregator Business Model
Business models for startups often include aggregator approaches in various industries. Aggregator models group services or products from different providers in one site. These businesses work as go-betweens for the consumers and the service givers.
Marketing, payments, and customer care are normally handled at the aggregator level. Revenue generation usually involves taking a percentage of each transaction.
Companies using the aggregator model:
- Grubhub
- Booking.com
- Expedia
- Zillow
In the US, Grubhub functions as an aggregator for meal delivery services. It offers online ordering and delivery services in collaboration with restaurants. Customers can quickly explore menus and place orders on Grubhub’s platform. The company handles payment processing and provides delivery logistics support.
This model allows businesses to create a user-friendly platform and manage multiple suppliers. It is less suitable for companies in industries with limited suppliers or low consumer demand. High competition and dependency on third-party providers can pose significant challenges.
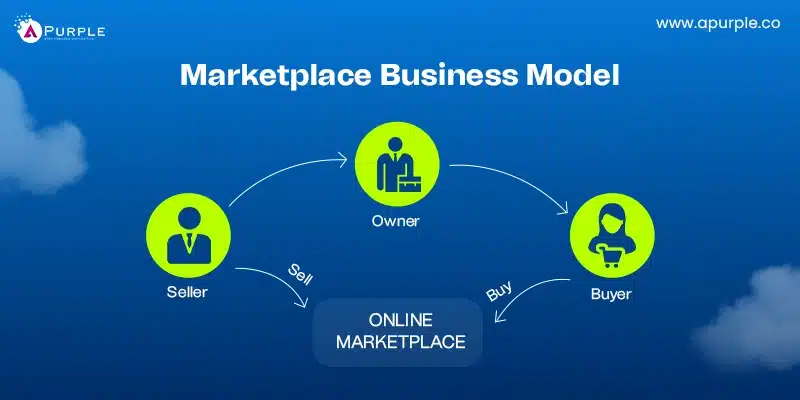
5. Marketplace Business Model
A marketplace business model focuses on providing a platform for customers and sellers to meet. Sellers not affiliated with the platform can upload goods and services for sale. The marketplace will generate income from transaction fees, subscriptions, or display ads.
Instacart is a grocery delivery service that connects customers with personal shoppers. These shoppers mostly get food from local stores and deliver it to customers. This model makes it possible to design a flexible, scalable service that does not require owning a stock of mobiles.
Airbnb is an application that allows property owners to open their spaces for rent to travelers. This form of P2P model offers various types of accommodations for the users. This form of business establishes a huge and comprehensive chain of hotels but with no actual properties.
Companies using this model:
- Amazon
- Fiverr
- Etsy
Each utilizes technology to manage transactions and enhance customer experience. This model thrives on building trust between buyers and sellers.
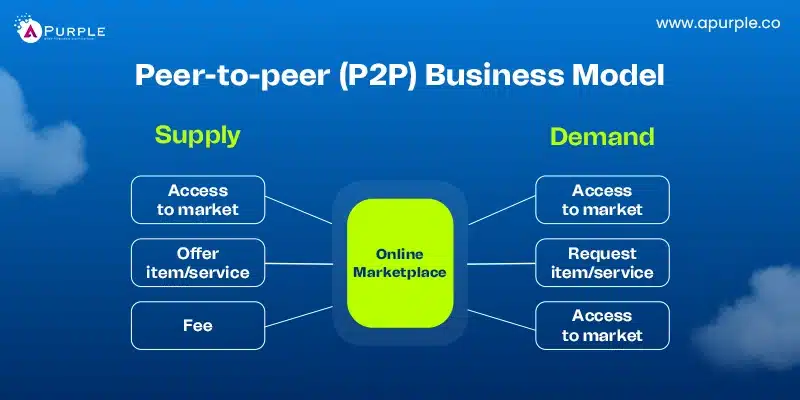
6. Peer-to-peer (P2P) Business Model
Peer-to-peer (P2P) exchanges allow people to trade goods and services directly. By reducing the need for middlemen, this model promotes a community-driven marketplace.
Lyft connects riders with drivers, providing convenient transportation solutions. Drivers use their vehicles and earn money by offering rides. This model leverages technology to match demand with supply efficiently.
Companies using this model:
- OLX
- Airbnb
- TaskRabbit
- LendingClub
This type of startup business model is ideal for situations where trust and openness are paramount. It is suitable for services such as ride-hailing applications, house rental services, or freelance services. This model will be ideal for industries that need to provide services to clients on a per-order basis.
However, the P2P model is not recommended for businesses that require compliance with specific legal requirements, such as those in the healthcare and finance industries.
7. Pay-As-You-Go Business Model
The pay-as-you-go business model allows customers to pay only for the services they use. This concept is very scalable and adaptable to users’ needs.
Companies using this model:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Uber
- Netflix
AWS charges users according to how much processing power they consume. This strategy is affordable for new companies and those with varying needs.
Pay-as-you-go services are well suited to cloud computing and streaming sectors. It is less suitable for businesses requiring upfront capital investment or fixed pricing models.
This approach promotes lean startup business model principles by offering cost control and flexibility.
It may not work well for high-stakes industries needing predictable revenue.
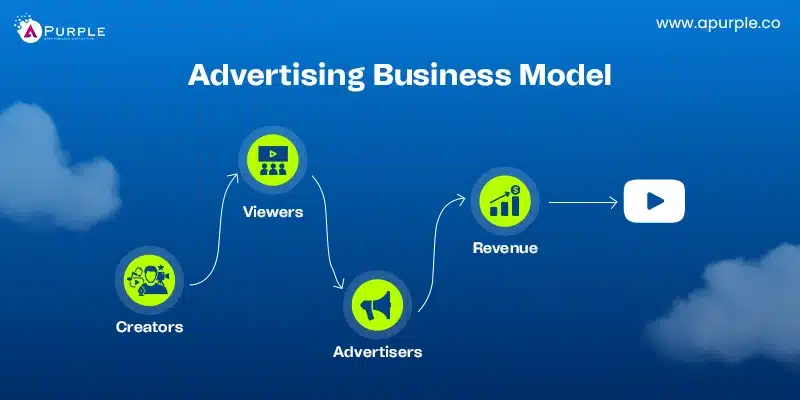
8. Ad-Based Business Model
The ad-based business model makes money by allowing users to display ads. Companies charge businesses for advertising space.
Companies using this model:
- YouTube
Google’s advertising platform, Google Ads, generates substantial revenue for the company. Advertisers pay to display their ads on websites and search results.
Facebook makes money through targeted advertising. User data helps deliver relevant ads, increasing engagement and ad revenue.
This business model is used by startup companies that work in industries with large user bases and high engagement. It is suitable for social media, search engines, and content platforms.
It may not suit businesses with niche audiences or low traffic. High dependency on user data can raise privacy concerns. It also requires continuous user engagement to sustain revenue streams.
9. Direct-to-Consumer Business Model
Bypassing mediators and selling goods directly to consumers is the direct-to-consumer business strategy.
Companies using this model:
- Warby Parker
- Dollar Shave Club
- Glossier
Warby Parker offers direct eyeglasses sales to customers both online and in-person. This strategy delivers competitive pricing while cutting expenses.
Dollar Shave Club provides customers with direct delivery of grooming goods through subscriptions. It makes shopping easier and increases client loyalty.
This model is suitable for brands wanting direct customer relationships and feedback. It suits industries like fashion, beauty, and personal care.
This startup business model may not suit businesses requiring extensive distribution networks or those reliant on physical retail presence. High upfront marketing costs and logistics management can be challenging. It works best for companies that can maintain efficient e-commerce operations.
10. Private Label Business Model
Under the private label business concept, goods made by other companies are sold under a company’s name. Businesses can manage pricing and branding using this strategy even without production facilities.
Companies using this model:
- AmazonBasics
- Trader Joe’s
- Kirkland Signature
A vast selection of reasonably priced goods are available under AmazonBasics’ private label. This tactic improves brand loyalty and consumer trust.
Trader Joe’s sells unique food items sourced from various suppliers under its brand. This creates exclusivity and differentiation in the market.
The private label model suits businesses that offer exclusive, branded products and is ideal for retailers seeking to develop a unique product line.
This business model may not suit companies lacking strong brand recognition. Reliance on outside manufacturers may need fixing for quality control. It also calls for a significant upfront expenditure in marketing and branding.
11. Franchise Business Model
Through the franchise business model, people can run a business using a company’s trademark and system. Franchisees profit from operational assistance and well-established branding.
Companies using this model:
- McDonald’s
- KFC
- Subway
McDonald’s provides a complete business package, including training and marketing. This ensures consistency across all locations.
KFC offers franchisees access to proprietary recipes and extensive operational support. This model leverages the brand’s global recognition.
The franchise model is ideal for industries like quick-service restaurants and retail. It provides entrepreneurs with a proven system, reducing their risk.
This model may not suit businesses seeking creative freedom or those with unique, niche offerings. High initial fees and ongoing royalties can be challenging. This model is best for those valuing structured support over innovation.
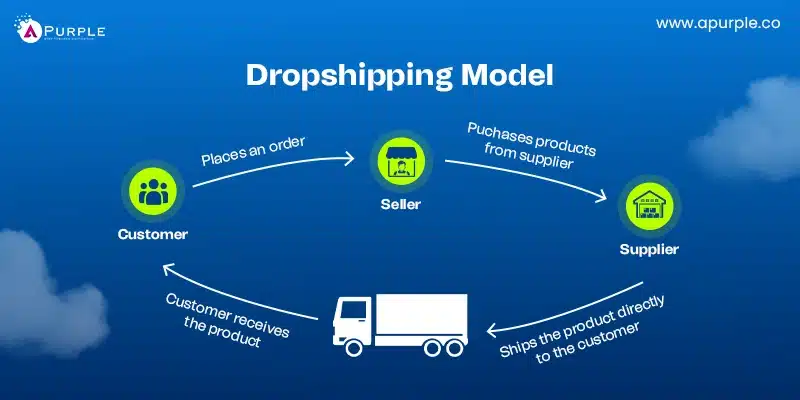
12. Dropshipping Business Model
Retailers that don’t have inventory can sell things by using the dropshipping business model. Third-party providers complete orders, which lowers overhead expenses.
Companies using this model:
- Oberlo
- Sprocket
- Printful
Oberlo helps entrepreneurs find products to sell online. It integrates with Shopify to ensure easy store management.
Spocket offers a range of US and EU products for dropshipping. This ensures faster shipping times for customers.
This model suits businesses with limited startup capital. It allows easy testing of new products and markets.
This business model may not suit companies seeking high profit margins. Dependence on suppliers can affect quality control. However, by minimizing initial investment and risk, this model aligns well with the principles of the lean startup business model.
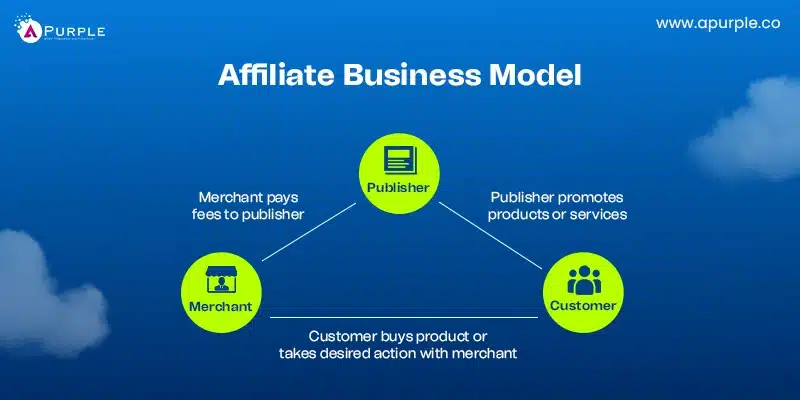
13. Affiliate Business Model
Affiliates in this business model receive commissions for promoting other businesses’ goods and services. They monitor sales and referrals using special links.
Companies using this model:
- Amazon Associates
- Rakuten Marketing
- ClickBank
Amazon Associates allows affiliates to earn by advertising Amazon products. Commissions are earned on each sale made through their links.
Rakuten Marketing connects affiliates with global brands. It offers a range of products and promotional tools.
Bloggers, influencers, and content producers will benefit from this arrangement, which is scaleable and requires little initial expenditure.
This business model may not suit businesses needing high profit margins. Success depends on high traffic and effective marketing strategies. Affiliates must comply with the companies’ policies to ensure continued partnerships. This model is best for those who excel in digital marketing and audience engagement.
14. Licensing Business Model
Companies can generate income by granting permission to use their intellectual property through the licensing business model. This can apply to technologies, trademarks, or patents
Companies using this model:
- Microsoft
- Disney
- Dolby Laboratories
Microsoft licenses its software to various hardware manufacturers. This model expands its market reach without manufacturing devices.
Disney licenses its characters and brands to merchandise producers, which generates substantial revenue from toys, apparel, and other products.
This model suits businesses with substantial intellectual property assets. It provides a steady income stream and expands brand presence.
This model may not suit startups with limited IP portfolios. Managing licenses and ensuring compliance can be complex. This model works best for companies with valuable, protectable assets looking to leverage their intellectual property without directly producing goods.
15. Crowdsourcing Business Model
A sizable population is tapped into via the crowdsourcing business model to provide ideas, services, or material. This model taps into a broad talent pool without traditional employment structures.
Companies using this model:
- Wikipedia
- Kickstarter
- Threadless
Worldwide volunteers are essential to creating and editing Wikipedia’s content. This technique does not require a large team to maintain vast, current knowledge.
Kickstarter allows creators to raise money for their ideas from the general public. This strategy offers financial support without the need for conventional investment.
This model suits businesses needing diverse input or funding from a broad audience. It is suitable for open-source projects, creative ventures, and problem-solving platforms.
It may not suit businesses requiring tight control over processes or proprietary information. Ensuring quality and consistency can be challenging. However, this model aligns well with the principles of the lean startup business model by minimizing costs and leveraging external resources.
Identifying the most suitable model from these business models for startups is critical for your startup’s success. It can have a direct effect on your business and its future. Use your industry, target audience, and competitive advantage when deciding.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Business Models
Appreciating the various business models is essential, especially for entrepreneurs. All the models have their advantages and disadvantages, which can make a vital difference in the success of a business. Below are the pros and cons of each of the startup business models that we have discussed in this blog:
| Business Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Freemium Business Model | Attracts large user base; low customer acquisition costs; rapid user growth | Conversion rate critical for profitability; continuous feature development |
| Subscription Business Model | Predictable revenue; ongoing customer relationships; opportunities for upselling | Requires continuous value delivery; emphasis on retention and satisfaction |
| On-demand Business Model | Real-time service delivery; leverages gig economy; high convenience | Pricing fluctuations, dependency on user ratings, logistic complexities |
| Aggregator Business Model | Centralized platform; standardized customer experience; economies of scale | Relies on provider quality, competitive market, complex logistics |
| Marketplace Business Model | Connects buyers and sellers; scalable; low inventory costs | High competition; platform management complexities |
| Peer-to-peer Business Model | Direct transactions; community-driven; scalable | Regulatory challenges; quality control issues |
| Pay-as-you-go Business Model | Flexible pricing; cost-effective; scalable | Revenue unpredictability requires continuous usage monitoring |
| Ad-based Business Model | Low-cost access to revenue; scalable | Privacy concerns: requires high user engagement |
| Direct-to-consumer Business Model | Control over branding, direct customer relationships, scalable | High marketing costs; logistics management |
| Private Label Business Model | Control over branding and pricing; lower production costs | Dependence on third-party manufacturers; high initial marketing costs |
| Franchise Business Model | Established brand recognition; operational support | High initial fees; ongoing royalties |
| Dropshipping Business Model | Low startup costs; no inventory management | Low-profit margins; dependency on suppliers |
| Affiliate Business Model | Minimal upfront investment; scalable | High competition; reliance on traffic and marketing strategies |
| Licensing Business Model | Steady income stream; expands market reach | Complex management; high compliance requirements |
| Crowdsourcing Business Model | Access to diverse talent and ideas, low costs | Quality control challenges require strong community management |
The correct model selection can make or kill a startup. It is critical to consider both the advantages and disadvantages to make judgments that align with company objectives.
Get the aPurple Advantage for Your Startup
Selecting the appropriate startup business model is essential to success. At aPurple, we specialize in custom, web, and mobile software. We provide customized solutions for both established businesses and startups.
We provide services such as:
- Software Product Development
- Mobile Application Development
- Website Design and Development
- Branding Service
Our expertise includes designing, developing, and deploying projects across various industries. For example:
- Taxi Booking App
- Telemedicine App
- eCommerce App
- Food Delivery App
Our experienced team helps startups decide on and implement the correct business model. Contact our experts to learn more about our startup solutions.
FAQs