Do you want to start your quick commerce business? Have you gone through successful quick commerce case studies? If the answer is YES, then you must have heard about Gopuff. It became a household name in the last decade or so because it focused on providing a seamless user experience. As a result, it received strong funding from VCs, which allowed it to expand into major cities.
But this is only the tip of the iceberg. As you dive deeper, you want to know: What is Gopuff beyond an on-demand delivery app? Is it a marketplace similar to DoorDash? Or does it have its own inventory? Having clarity on these things matters a lot because it directly affects your profit margin, cash burn, and control over the platform. This leads to the next question: How does Gopuff work across fulfillment platforms and revenue streams?
We have written this blog to answer all of your questions. By reading this blog, you will learn about Gopuff’s business model, logistics workflow, monetization strategy, and technical foundation. Based on these details, you can easily analyze whether building a similar app or platform is financially viable for your startup.
What is Gopuff?
Gopuff is a digital delivery service and retailer founded in 2013 by Yakir Gola and Rafael Ilishayev. It delivers convenience items such as snacks, drinks, household essentials, over-the-counter medicines, and, in some markets, alcohol to customers within a few minutes.
Gopuff operates through its network of local micro-fulfillment centers. Rather than relying on third-party stores, Gopuff owns and manages its own inventory, allowing it to deliver products faster, ensure a consistent user experience, and maintain full control over operations.
How does Gopuff work?
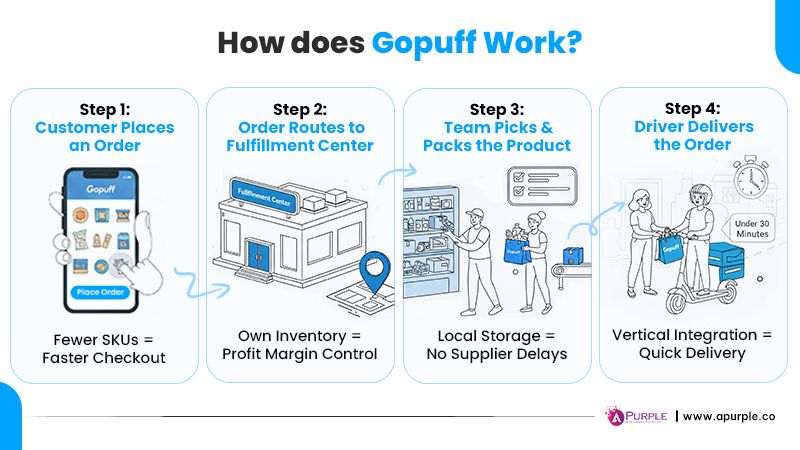
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of “how does Gopuff delivery work” behind the scenes:
Step 1: Customer Places an Order in the Application
When you carefully analyze the inner workings of the Gopuff application, you will realize that the workflow begins with the customer opening the app, browsing available products, placing an order, and checking out.
Gopuff keeps a limited number of products in the application because fewer SKUs mean faster checkout and better demand forecasting. It also helps streamline operations early on.
Step 2: Order Routes to Nearest Fulfillment Center
Once the customer places an order, it is routed to the nearest fulfillment center/dark store based on the customer’s delivery location.
As Gopuff has its own inventory center, it can reduce vendor delays, ensure fast delivery, and control pricing.
Step 3: In-House Team Picks and Packs the Product
The in-store team receives the order details and, based on them, picks and packs the appropriate products within minutes.
Because the products are stored locally, there is no need to communicate with the supplier, ensuring the fastest possible delivery.
Step 4: Driver Accepts the Delivery Request and Delivers the Order
Once the order is ready for dispatch, nearby drivers receive the delivery request, accept it, and deliver the order to the appropriate destination.
Because of its vertical integration, the Gopuff delivery service can keep delivery times within 30 minutes.
What is Gopuff’s Business Model?
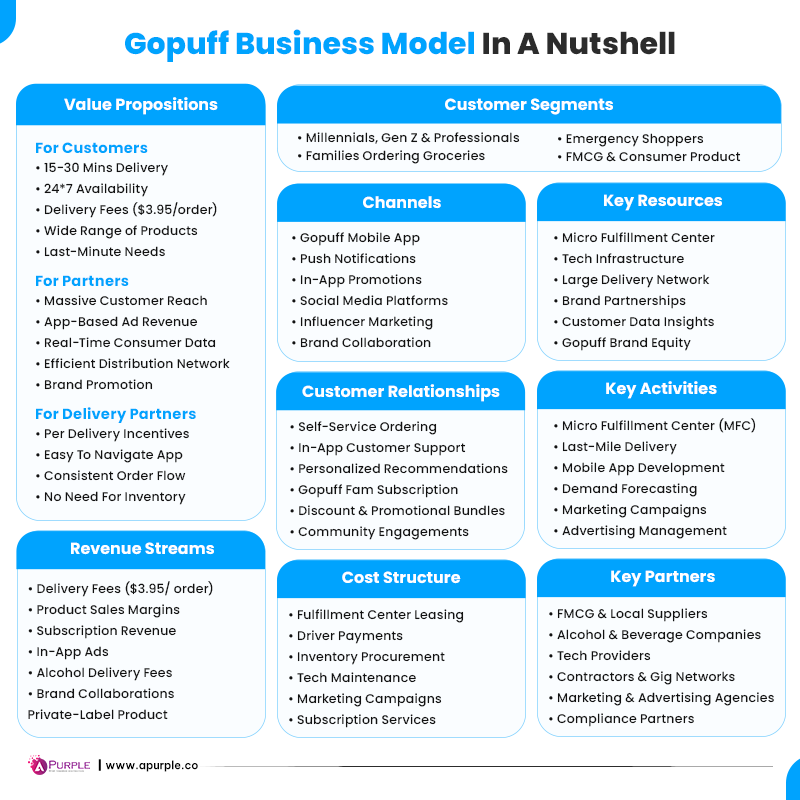
Gopuff basically operates on the principle of vertical integration in the quick commerce space. So, it has complete control over fulfillment, inventory, and delivery. Based on this idea, Gopuff has developed its business model. Let’s dive deeper into how GoPuff creates, delivers, and captures value for its customers, partners, and delivery persons.
You must have a basic understanding of how Gopuff operates at a business level, based on the image above.
However, that is just basic information. But the question for any startup founder will be: why does it matter to me, and what are the key things to learn from Gopuff’s business model? So, here’s the founder-focused breakdown:
| Business Model Block | Description | Lesson For Founders |
|---|---|---|
| Value Proposition | Gopuff ensures 15 to 30-minute delivery by stocking products in its own micro-fulfillment centers. | Inventory control is your USP, not speed. If you have total control over inventory, you can ensure faster delivery and a world-class user experience. |
| Customer Segments | Urban, densely-populated areas. Students, young professionals, and families who want convenience goods delivered to their homes. | Choosing the right customer segment is vital to sustaining your business over the long term. Choose the one that can give your repeated orders. |
| Channels | Mobile app, email, social media, push notification, and influencer marketing. | Customer retention matters more than acquisition. You need an omnichannel presence and should focus on personalization and quick responses. |
| Customer Relationships | Subscription program, combo packages, and targeted discounts. | You should always offer subscription plans and provide lucrative discounts to your customers, as this will create a steady revenue stream. |
| Key Partners | FMCG brands, alcohol distributors, gig drivers, compliance partners, and technology partners. | You should focus on establishing brand partnerships to help you generate advertising revenue. |
| Key Activities | Inventory management, warehouse management, route optimization, demand forecasting, and last-mile delivery | As a startup founder, streamlining your operations is a must in a highly competitive convenience-delivery market. |
| Key Resources | Micro-fulfillment centers, delivery network, tech infrastructure, and demand data. | The number of orders basically drives your revenue. So, select the right market and establish all necessary resources in advance before going operational. |
| Revenue Streams | Delivery fees, subscription charges, sponsored listings, private-label products, and alcohol commissions. | You can’t rely on one revenue channel in a highly competitive market. So, diversifying the revenue stream will help you build a profitable business. |
| Cost Structures | Driver payments, warehouse lease, insurance, technology development, marketing, and inventory management. | The convenience-delivery market comes with high fixed costs. So, you shouldn’t scale too fast as it will burn your cash. Start with one city and establish yourself before moving to other cities. |
How does Gopuff Make Money?
Ultimately, running each business for a startup owner is about profitability. So, let’s understand how Gopuff makes money by analyzing its revenue streams and monetization strategies.
| Monetization Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Retail Product Markup | Gopuff generally buys inventory at wholesale prices and sells it to customers at retail prices. This difference between the buying and the selling price is the primary source of revenue for Gopuff. |
| Delivery Fees | Customers must pay a delivery fee for each order, which varies based on product demand, customer location, and logistics costs. |
| Subscription Model | Gopuff Fam is a monthly subscription service for customers that offers benefits such as free delivery and discounts. It increases the number of orders, uplifts customer retention, and creates recurring revenue. |
| Small Order & Surge Fees | Customers must pay extra fees for low-value orders or high-demand products, which also adds to Gopuff’s revenue model. |
| Brand Advertising & Promotions | Brands that want to leverage Gopuff’s reach request feature listing, in-app advertising, and sponsored listing, which creates a high-margin revenue source. |
| Private Label Products | Gopuff also focuses on introducing its in-house brand and creating its own products, which provide higher profit margins. |
What are the Key Features that Make Gopuff Successful?
Here are the core features that have made Gopuff a household name in the last few years:
| Key Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Dark Stores | Instead of relying on third-party warehouses, Gopuff invested heavily in small-scale fulfillment centers, which helped maintain higher availability, faster delivery, and higher profit margins. |
| Inventory Ownership | From the very beginning, Gopuff owned its inventory, which allowed it to offer better pricing, introduce private-label products, and achieve higher profits. |
| Flat Delivery Fee | Gopuff has set a flat delivery fee rather than varying it by location, which encourages users who are far away to order from them rather than competitors. |
| Data-Driven Demand Forecasting | By knowing product demand in advance, you can keep your inventory levels up to date, which becomes a massive factor in overall profitability. |
| Optimized Driver Workflow | The driver needs to pick up the parcel directly from the nearby fulfillment center rather than from a third-party warehouse, thereby reducing idle time. |
| High-Frequency Product Mix | Gopuff emphasizes stocking products that customers buy repeatedly, such as snacks, OTC medicines, alcohol, and household essentials. |
| Mobile-First Experience | Faster checkout, personalized recommendations, push notifications, and saved carts enhance the user experience, which is critical in grocery delivery app development. |
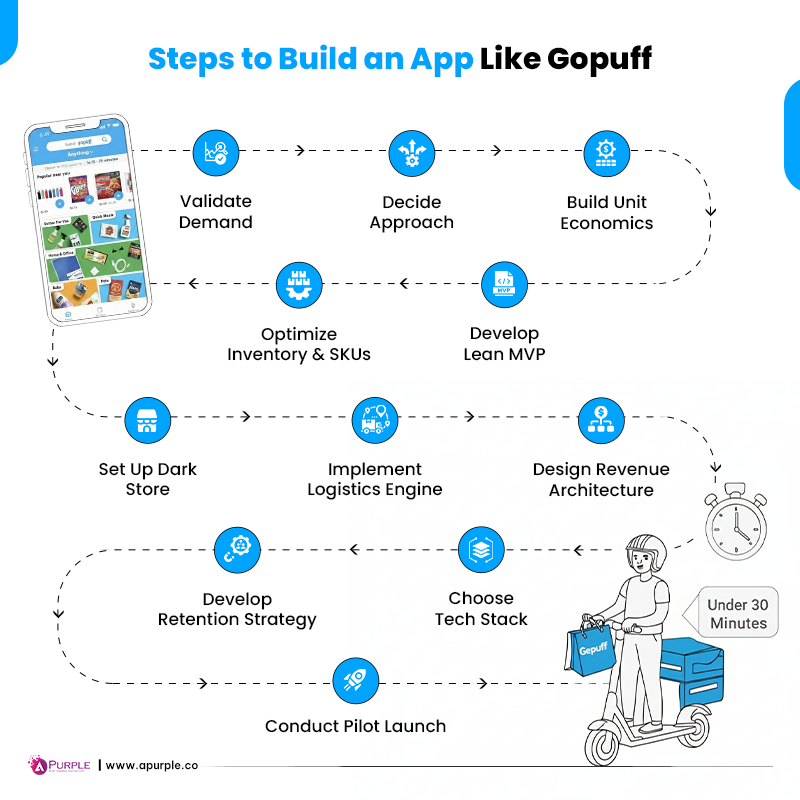
How to Build an App Like Gopuff?
So far, you have understood how Gopuff works, its business model, how it makes money, and the key drivers of that revenue. Based on this analysis, you must have thought about building an app like Gopuff, haven’t you? So, let’s turn your idea into reality and provide you with a detailed roadmap for building an app like Gopuff.
Step 1: Validate Your Demand
You should start by picking 3-5 highly populated areas and finding out their average household income, the number of rental properties, and the average delivery time of competitors.
You can also create a landing page and analyze the signup rate to see whether your idea resonates with people.
If your target market is giving you around 8-15 orders per hour, then your business will survive. Otherwise, your model will not survive despite using the best technology.
Step 2: Decide Your Approach
You need to decide whether to opt for an inventory-owned dark store model or a marketplace model. To that end, you can create financial projections based on gross margin, operating costs, and capital requirements to provide a fair comparison.
Also, you can make these decisions based on whether you are ready to invest a hefty amount in inventory to have complete control, or you want a lower upfront cost and are ready to accept a thin profit margin. If you choose the first option, opt for a dark store model; otherwise, choose a marketplace model.
Step 3: Build a Unit Economics Model
You should break down the per-order cost, which comprises factors such as product cost, delivery cost, payment processing fees, labor cost, marketing, etc. After determining the per-order cost, calculate the per-order profit margin.
If you can achieve a positive profit margin per order before scaling, you should continue with your business idea. Otherwise, you need a massive shift in your SKUs, pricing strategy, or delivery radius before starting the development phase.
Step 4: Develop a Lean MVP
If you’ve reached this step, all your prerequisites are pretty sorted. So, now it’s time to use the Lean Startup methodology to build an MVP. For that purpose, define must-have features, i.e., Admin Panel (pricing, inventory management, order monitoring), Customer App (search, checkout, reorder, cart), and Delivery Partner App (accept orders, earning tracking, navigation).
Don’t build any features to impress investors. Instead of that, focus on building features that can help you validate the repeat frequency of orders.
Step 5: Optimize Your Inventory and SKUs
You should always start with 1500-3000 SKUs that are most likely to receive repeat orders. Focus on day-to-day essentials and impulsively bought products. Don’t try to expand your SKUs in the initial phase; instead, focus on saving cash by choosing fast-moving inventory.
Step 6: Set Up Your Dark Store Infrastructure
Begin by leasing 2-3 nearby fulfillment centers in a densely populated area. Design your dark store layout to complete deliveries within 5 minutes. Lastly, install any basic warehouse management software and define SOPs for order pickup and delivery. Try to become the king of a micro-market first before expanding to multiple zones.
Step 7: Implement Your Logistics Engine
You should start by integrating route optimization software into your ecosystem. Define order batching logic, geo-fencing delivery zones, and driver shift planning. Lastly, decide whether to optimize for a 10-minute delivery at a higher cost, or settle for a 20-30-minute delivery, which is more sustainable.
Step 8: Design Your Revenue Architecture
Clearly define your revenue streams, including delivery fees, subscription models, per-product profit margins, and surge pricing. You also need to decide whether you want to compete purely on price by burning through all your capital or settle for a brand that focuses more on user experience.
Step 9: Choose Your Tech Stack
You should always choose technologies that help you to facilitate scalability, flexibility, and security. For that purpose, you can opt for these options:
- Backend: Node.js, Go, RoR
- Cloud: AWS, GCP, Azure
- Database: PostgreSQL, Firebase, Redis
- Payment Processing: Stripe, PayPal, Square
Always build infrastructure that can help you grow your business by 10x, rather than one that requires a complete rebuild within 12 months.
Step 10: Develop a Customer Retention Strategy
You should design referral loops, offer promo codes, and provide subscription incentives to increase customer retention. You need to know whether your repeat-customer ratio is high enough to cover the acquisition cost. If the answer is YES, you can spend a significant amount to market your application, but if the answer is NO, full-fledged marketing can burn cash.
Step 11: Conduct a Pilot Launch
If everything is in order at this stage, carry out a pilot launch in a specific zone and measure order frequency, customer churn rate, delivery cost per order, and profit margin. If numbers are impressive, you can launch your application in other targeted markets.
How AI is Redefining Apps Like Gopuff?
AI is no longer optional; it is a necessity in any convenience-delivery app. Here’s how AI is redefining applications like Gopuff and making them smarter and personalized:
| Feature Powered By AI | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Demand Forecasting | AI can help you know the products that will be in massive demand in your neighbourhood so that you’re never out of stock. |
| Dynamic Pricing | AI will adjust pricing based on real-time product supply and demand, helping you protect your profit margin. |
| Smart Routing | AI can help you optimize delivery routes in real time using live traffic data to reduce delivery time and operating costs. |
| Inventory Intelligence | With the help of AI, you can know the fast-moving and slow-moving items to realign stocking decisions. |
| Personalization Engine | AI will recommend products to your customers based on their previous purchases, search patterns, and wish lists to increase order size. |
How aPurple Can Help Build an App Like Gopuff?
The convenience-delivery market is booming worldwide, as today’s customers expect everything delivered to their doorsteps within minutes. This shift can be a real opportunity for startup founders like you to cash in on. However, turning this opportunity into a profitable business model is not as easy as it sounds.
There are challenges such as high operating costs, inventory management risks, warehouse setup and lease costs, and 30-minute last-mile delivery. Overcoming these challenges while still keeping your business profitable is where most startup founders scratch their heads.
That’s where aPurple can be your best bet. We help startup founders like you turn your vision into a sustainable convenience-delivery business model by validating demand in your target market through a lean MVP, while protecting your hard-earned cash. We also help you plan logistics, inventory, revenue, and tech architecture before development begins.
Ready to build a convenience-delivery app that can scale seamlessly and stay profitable? Then, connect with us and share your requirements.